Luna, the earth moon, words from myths
(Diana, or Luna, Roman goddess of the Moon, animals, and hunting)
Diana or Luna; earth's moon
Luna gives us “lunar” from Latin lucere, to shine.
Symbol: a crescent Moon.

- Called Luna by the Romans, Selene and Artemis by the Greeks, and many other names in other mythologies.
- The twin sister of Apollo was Artemis; also known as Diana, Phoebe, Selene, or Cynthia; goddess of the Moon, of maidens, of hunting (the chase), and daughter of Zeus and Latona.
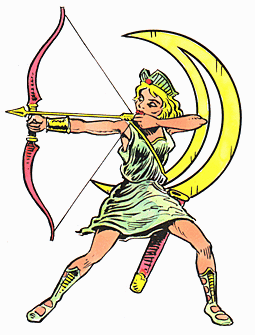
- In works of art, this goddess is generally represented as a beautiful maiden, clad in a short hunting dress, armed with a bow, a quiver full of arrows at her side, and a crescent on her well-poised head.
- The sudden deaths of women were attributed to her shafts; but, she was, also, a goddess of healing.
- She was often represented as a huntress, with hunting dogs and a boar’s head at her side.
- Diana is described as guiding her silvery chariot over the sky at night.
- She had three aspects: Diana in the heavens, Luna on earth, and Hecate, goddess of witchcraft, in the underworld.
- Moon and Earth, tied together by gravitational attraction, revolve as a double planet.
- Total eclipses occur when the Moon and Earth line up perfectly with the Sun.
- During a solar eclipse, the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, hiding the Sun on a small area of Earth.
- During a lunar eclipse, the full Moon moves into Earth’s shadow and is blacked out.
- Because Earth spins faster than the Moon revolves, the Moon rises an average of 50 minutes later each night.
- During the new phase, Moon and Sun rise and set at the same time; but, from then on, the Moon appears in different parts of the sky: in the west as it waxes larger towards gibbous, in the east as it wanes smaller.
- The gravitational force of the Moon, and to a lesser extent the Sun, raises the ocean tides on Earth.
- A great bulge of water is pulled up on the side of the Earth facing the Moon and held there.
- As Earth rotates beneath the bulge, high tides occur and then because of Earth’s rotation, the tide seems to move from east to west.
- None of the other planets has a moon like the Earth. Mercury and Venus have no moons at all, and Mars is orbited only by two tiny chunks of rock, each just one ten-millionth the size of Earth’s moon.
- Because the Moon rotates on its axis in exactly the time it takes to orbit the Earth, it always presents the same side to us.
- The Moon does not emit light. What we see is sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface as the Moon goes through its familiar phases.
A few scientific facts about the Moon and the Earth
 The page of planet images.
The page of planet images.
A cross reference of word units that are related, directly or indirectly, to the: "moon": Calendar, Moon Facts; Chemical Element: selenium; Gods and Goddesses; luna, luni-; menisc-; meno-; Planets in Motion; plano-; seleno-.
