mite, mites +
(Old English: a small or tiny insect; acurus)
2. Any arthropod of the order acarina, except the ticks which are among the most diverse and successful of all the invertebrate groups: When cleaning out her pantry, Jill found some mites which were infesting her potatoes and pasta.
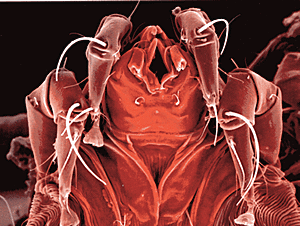
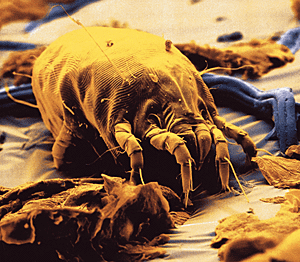
Common name for most members of the arthropod order Acarina
They are minute animals related to the spiders, usually having transparent or semitransparent bodies. They may be parasitic on man and domestic animals, producing various irritations of the skin (acariasis or mite infestations). Many mite species are important to human and veterinary medicine as both parasite and vector (organism capable of conveying an infection that produced the disease from one host to another).
Mites have exploited an incredible array of habitats and because of their small size (some are microscopic) most go totally unnoticed. Many live freely in the soil or water, but there is also a large number of species that live as parasites on plants or animals (including humans).
Most kinds of mite are free-living, predatory soil dwellers, feeding on various invertebrates, soil microbes, insect eggs, and other organisms. Many are parasitic for at least part of their life cycles, feeding on the skin and blood of vetebrates. Others are permanent obligate parasites living within the skin.
Cross references of word families that are related directly, or indirectly, to: "spider; arachnoidea": acaro-; arachno-; arano-.
