medico-, medic-, medi-, med-
(Latin: heal, cure, remedy; physician, doctor; practice of medicine, give medicine to)
2. A reference to a medicine or to healing.
2. The act and science of the diagnosis and treatment of disease and the maintenance of health; as well as, the prevention of illness.
3. Treatment of disease by medical, as distinguished from surgical actions; nonsurgical treatment.
There are several varieties of medicine which include: adolescent, aerospace, alternative, aviation, Ayurvedic, behavioral, clinical, community, cookbook, defensive, diagnostic nuclear, dental, disaster, domestic, emergency, environmental, experimental, family, fetal and maternal, folk, forensic, geographical, geriatric, group, high-tech, holistic, humanistic, hyperbaric, industrial, integrated, internal, legal, manipulative, mental, neonatal, nuclear, occupational, oral, osteopathic, patent, perinatal, physical, physical and rehabilitation, preclinical, preventive, proprietary, psychological, psychosomatic, social, socialized, space, sports, state, tropical, veterinary, and whole person.
There is no doubt that other specialized medical areas also exist.
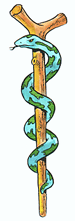
Latin: Aesculapius (god)
The Aesculapius staff is considered to be the appropriate symbol of medicine, not the Mercury caduceus. The Mercury symbol is incorrectly used by many U.S. medical organizations; especially by military units.
2. Medical Insurance, which is also known as mediclaim in which the policy holder is entitled to receive the amount spent for his health purposes from the insurance company.
3. Insurance that covers most serious medical expenses up to a maximum limit, usually after a deductible and co-insurance have been met.
3. A type of insurance coverage that pays for medical and surgical expenses that are incurred by the insured.
Health insurance has many relatives; such as, disability insurance, critical (catastophic) illness insurance, and long-term care (LTC) insurance.
4. Apparently, the term Mediclaim Insurance is used more often in India with the meaning of: Hospitalisation for illness, disease or accident, whether including surgery or not, which imposes a heavy financial burden on individuals, families, employers, and welfare bodies.2. The study and science of the newborn up to two months of age postnatally.
3. The branch of medicine dealing with the newborn infant and its diseases, as well as its physical and psychological care, assessment, and development.


